

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 1917-1931.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2023.01917
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
YIN Huazhan1,2,3, ZHANG Li1,2( ), LIU Pengyu1,2, LI Dan1,2(
), LIU Pengyu1,2, LI Dan1,2( )
)
Received:2023-01-12
Published:2023-12-25
Online:2023-10-16
Contact:
ZHANG Li, E-mail: YIN Huazhan, ZHANG Li, LIU Pengyu, LI Dan. (2023). How the dimension of negative emotional motivation influences time perception: The mediating role of attention control and attention bias. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(12), 1917-1931.
| dimension (math.) | converge to a limit (in calculus) | evade (an issue) | unisex |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Motivation Dimension | 6.81 ± 0.70 | 2.84 ± 0.62 | 4.98 ± 0.46 |
| pleasantness | 2.79 ± 1.13 | 2.66 ± 0.67 | 5.00 ± 0.54 |
| arousal | 6.19 ± 1.16 | 6.05 ± 1.20 | 2.97 ± 1.19 |
Table 1 Evocation of the three emotional pictures (M ± SD)
| dimension (math.) | converge to a limit (in calculus) | evade (an issue) | unisex |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Motivation Dimension | 6.81 ± 0.70 | 2.84 ± 0.62 | 4.98 ± 0.46 |
| pleasantness | 2.79 ± 1.13 | 2.66 ± 0.67 | 5.00 ± 0.54 |
| arousal | 6.19 ± 1.16 | 6.05 ± 1.20 | 2.97 ± 1.19 |
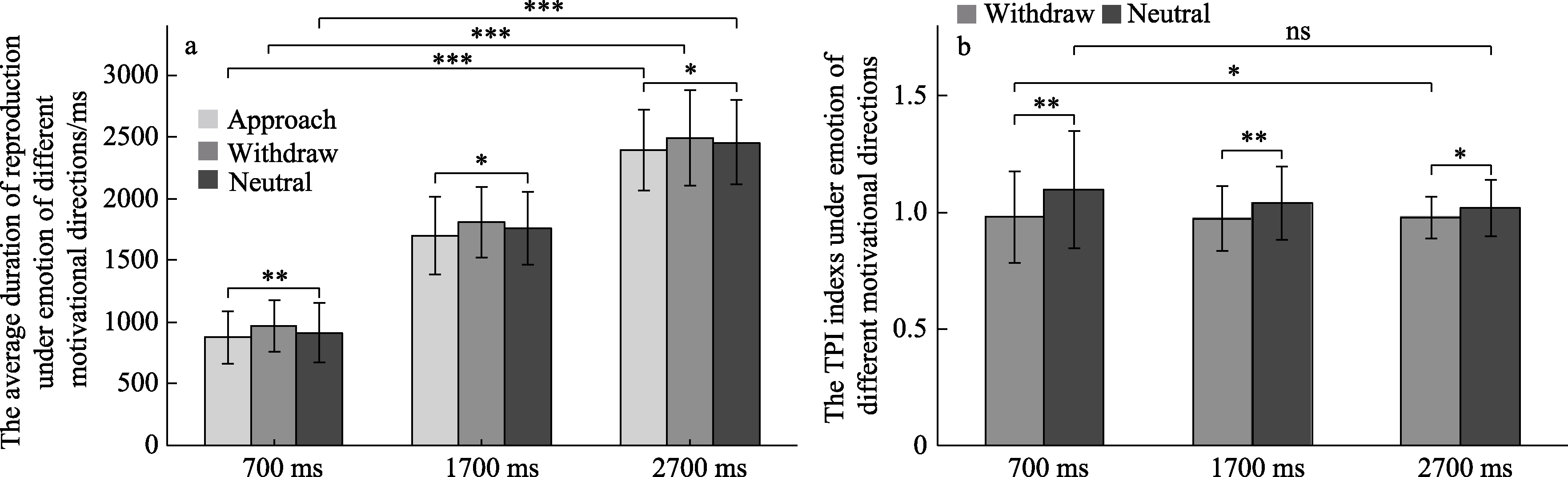
Figure 2. The average duration of reproduction and TPI indexs under emotion of different motivational directions. Note. Error lines are SD. * represents p < 0.05, ** represents p < 0.01, *** represents p < 0.001.
| Emotional type | ipsilateral | laterality |
|---|---|---|
| converge to a limit (in calculus) | 400.23 ± 114.25 | 453.91 ± 124.89 |
| evade (an issue) | 397.60 ± 112.18 | 422.01 ± 118.35 |
| unisex | 431.68 ± 108.58 | |
Table 2 Subjects’ response times (M ± SD) at different motivational orientation pictures and probe point types
| Emotional type | ipsilateral | laterality |
|---|---|---|
| converge to a limit (in calculus) | 400.23 ± 114.25 | 453.91 ± 124.89 |
| evade (an issue) | 397.60 ± 112.18 | 422.01 ± 118.35 |
| unisex | 431.68 ± 108.58 | |
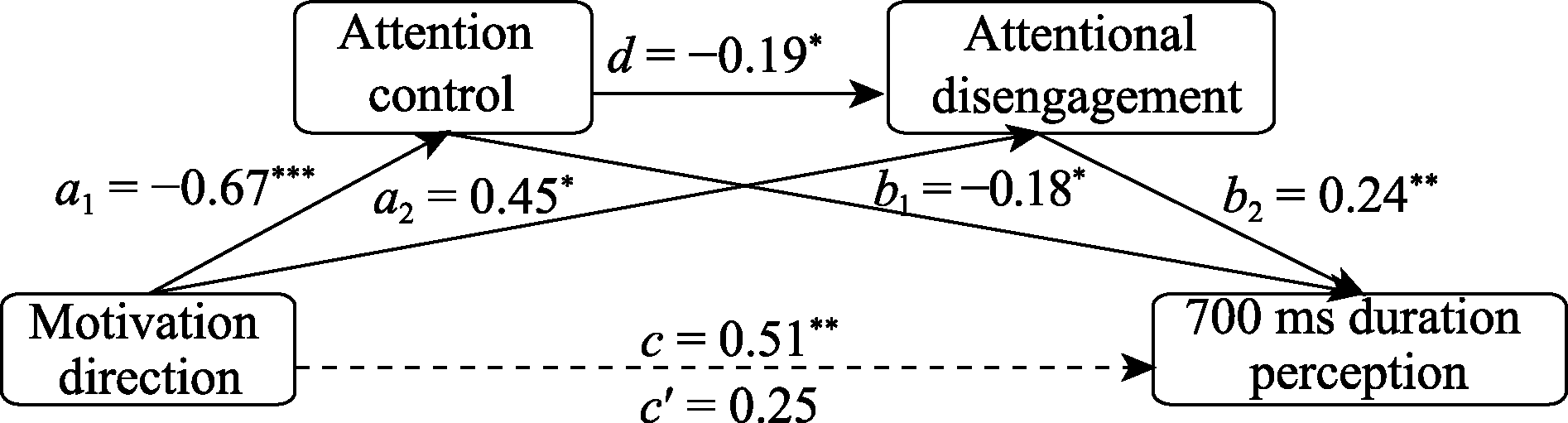
Figure 3. Chain mediation between attentional control and attentional disengagement in the direction of emotional motivation affecting 700 ms perception.
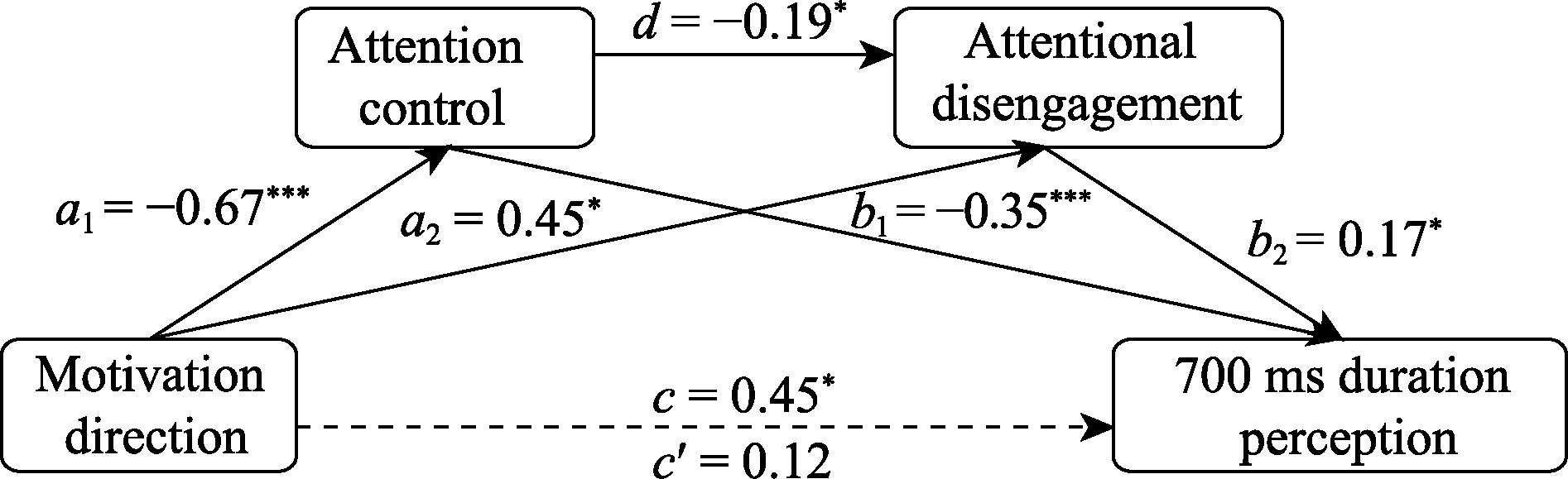
Figure 4. Chain mediation between attentional control and attentional disengagement in the direction of emotional motivation affecting 1700 ms perception.
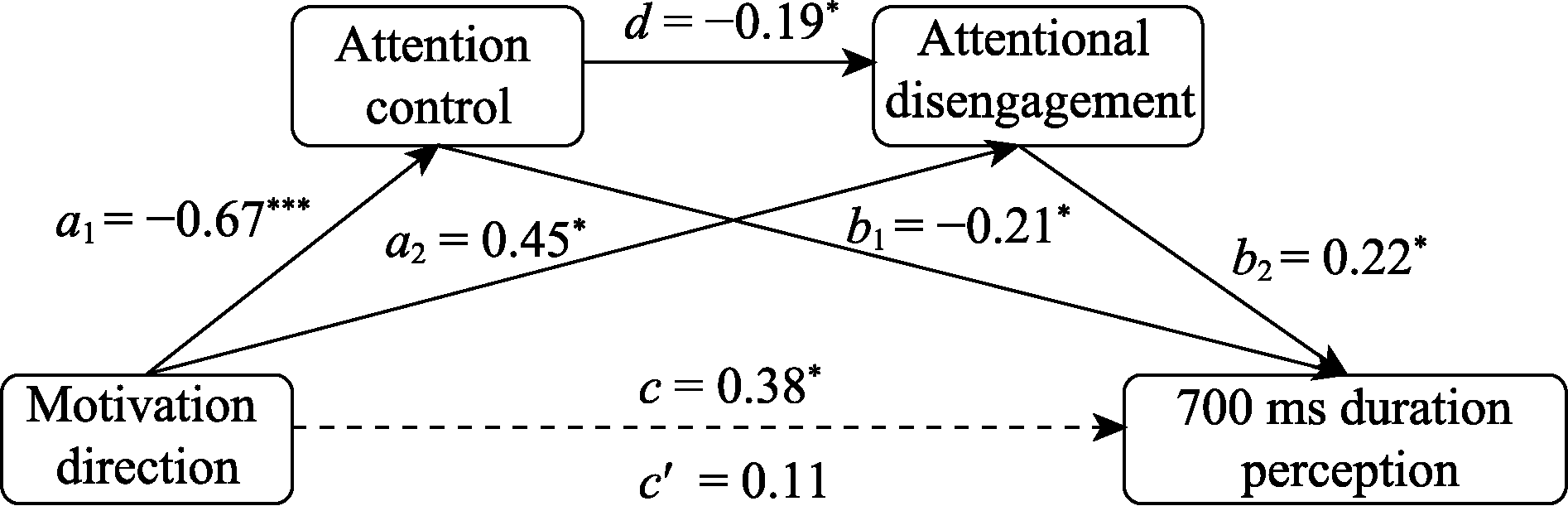
Figure 5. Chain mediation between attentional control and attentional disengagement in the direction of emotional motivation affecting 2700 ms perception.
| dimension (math.) | high withdraw | low evasion | unisex |
|---|---|---|---|
| motivation | 2.46 ± 0.76 | 3.53 ± 1.29 | 5.23 ± 0.61 |
| pleasantness | 2.53 ± 0.92 | 2.67 ± 1.05 | 5.44 ± 0.65 |
| arousal | 6.15 ± 1.18 | 5.95 ± 1.34 | 2.90 ± 1.32 |
Table 3 Evocation of the three emotional pictures (M ± SD)
| dimension (math.) | high withdraw | low evasion | unisex |
|---|---|---|---|
| motivation | 2.46 ± 0.76 | 3.53 ± 1.29 | 5.23 ± 0.61 |
| pleasantness | 2.53 ± 0.92 | 2.67 ± 1.05 | 5.44 ± 0.65 |
| arousal | 6.15 ± 1.18 | 5.95 ± 1.34 | 2.90 ± 1.32 |
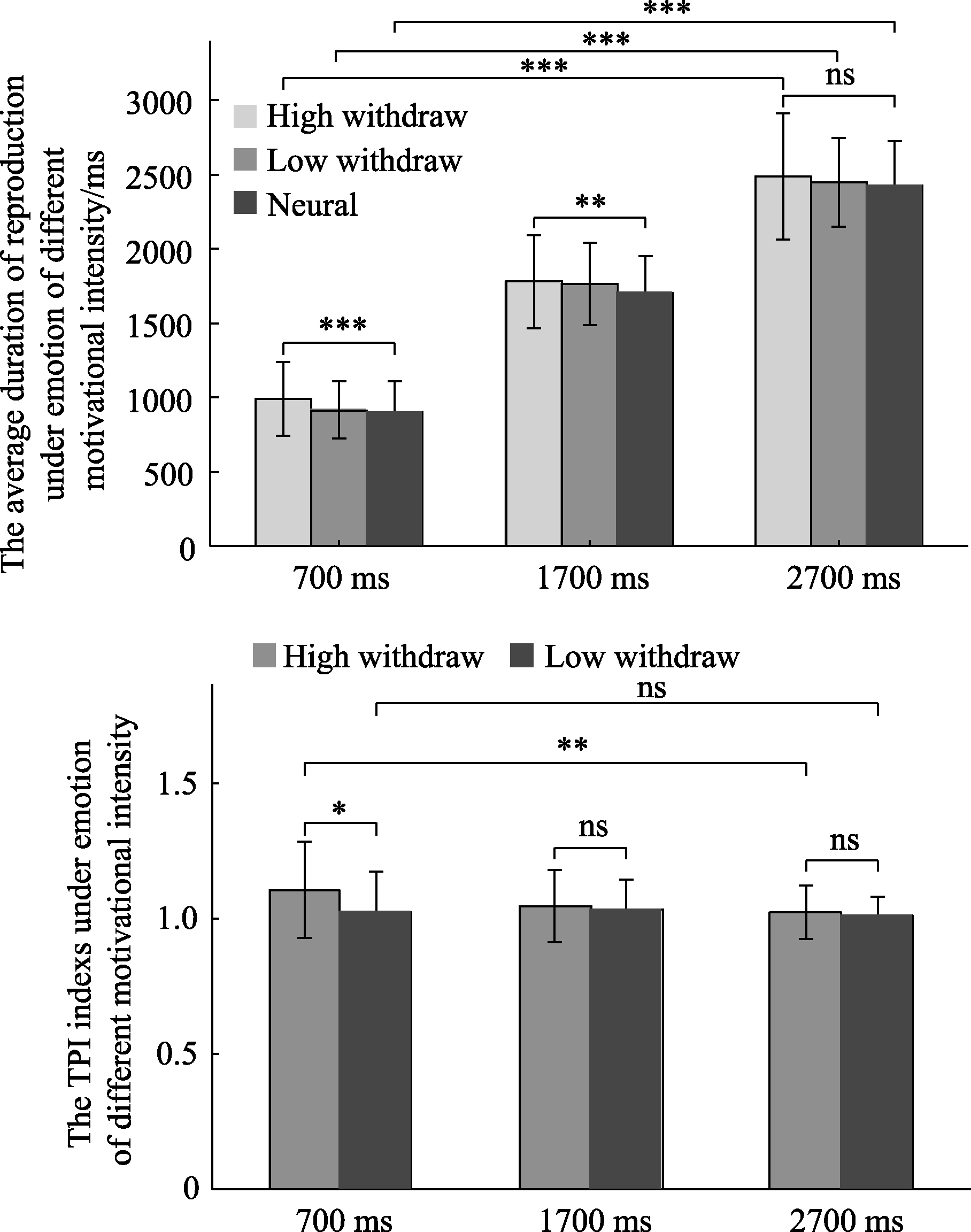
Figure 6. The average duration of reproduction and TPI indexs under emotion of different motivational intensity. Note. Error lines are SD. * represents p < 0.05, ** represents p < 0.01, *** represents p < 0.001.
| Emotional type | ipsilateral | laterality |
|---|---|---|
| high withdraw | 390.49 ± 111.04 | 422.02 ± 123.64 |
| low evasion | 415.50 ± 127.52 | 430.91 ± 125.85 |
| unisex | 432.37 ± 120.27 | |
Table 4 Subjects' response times (M ± SD) at different motivational intensity pictures and probe point types
| Emotional type | ipsilateral | laterality |
|---|---|---|
| high withdraw | 390.49 ± 111.04 | 422.02 ± 123.64 |
| low evasion | 415.50 ± 127.52 | 430.91 ± 125.85 |
| unisex | 432.37 ± 120.27 | |
| [1] |
Angrilli, A., Cherubini, P., Pavese, A., & Manfredini, S. (1997). The influence of affective factors on time perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 59(6), 972-982.
doi: 10.3758/BF03205512 URL |
| [2] |
Ashley, V., & Swick, D. (2019). Angry and fearful face conflict effects in post-traumatic stress disorder. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 136.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00136 pmid: 30804838 |
| [3] |
Benau, E. M., & Atchley, R. A. (2020). Time flies faster when you’re feeling blue: sad mood induction accelerates the perception of time in a temporal judgment task. Cognitive Processing, 21(3), 479-491.
doi: 10.1007/s10339-020-00966-8 pmid: 32206937 |
| [4] |
Bishop, S. J. (2009). Trait anxiety and impoverished prefrontal control of attention. Nature neuroscience, 12(1), 92-98.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2242 pmid: 19079249 |
| [5] |
Bishop, S., Duncan, J., Brett, M., & Lawrence, A. D. (2004). Prefrontal cortical function and anxiety: controlling attention to threat-related stimuli. Nature Neuroscience, 7(2), 184-188.
doi: 10.1038/nn1173 pmid: 14703573 |
| [6] |
Brosch, T., Sander, D., & Scherer, K. R. (2007). That baby caught my eye... Attention capture by infant faces. Emotion, 7(3), 685-689.
pmid: 17683225 |
| [7] |
Buhusi, C. V., & Meck, W. H. (2009). Relative time sharing: new findings and an extension of the resource allocation model of temporal processing. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 364(1525), 1875-1885.
doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0022 URL |
| [8] |
Campbell, L. A., & Bryant, R. A. (2007). How time flies: a study of novice skydivers. Behaviour research and therapy, 45(6), 1389-1392.
pmid: 16860291 |
| [9] |
Cisler, J. M., & Koster, E. H. (2010). Mechanisms of attentional biases towards threat in anxiety disorders: An integrative review. Clinical psychology review, 30(2), 203-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2009.11.003 pmid: 20005616 |
| [10] | Cui, X., Tian, Y., Zhang, L., Chen, Y., Bai, Y., Li, D.,... Yin, H. (2022). The role of valence, arousal, stimulus type, and temporal paradigm in the effect of emotion on time perception: A meta-analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 1-21. |
| [11] | Curtis, V., & de Barra, M. (2018). The structure and function of pathogen disgust. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 373(1751), 20170208. |
| [12] |
Droit-Volet, S., Brunot, S., & Niedenthal, P. (2004). BRIEF REPORT Perception of the duration of emotional events. Cognition and emotion, 18(6), 849-858.
doi: 10.1080/02699930341000194 URL |
| [13] | Elliot, A. J. (2013). Handbook of approach and avoidance motivation. Psychology Press |
| [14] |
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G* Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior research methods, 39(2), 175-191.
doi: 10.3758/BF03193146 URL |
| [15] |
Finucane, A. M. (2011). The effect of fear and anger on selective attention. Emotion, 11(4), 970-974.
doi: 10.1037/a0022574 pmid: 21517166 |
| [16] |
Gable, P. A., & Harmon-Jones, E. (2010). The motivational dimensional model of affect: Implications for breadth of attention, memory, and cognitive categorization. Emotion and Cognition, 24, 322-337.
doi: 10.1080/02699930903378305 URL |
| [17] |
Gable, P. A., & Poole, B. D. (2012). Time flies when you’re having approach-motivated fun: Effects of motivational intensity on time perception. Psychological science, 23(8), 879-886.
doi: 10.1177/0956797611435817 URL |
| [18] |
Gable, P. A., Neal, L. B., & Poole, B. D. (2016). Sadness speeds and disgust drags: Influence of motivational direction on time perception in negative affect. Motivation Science, 2(4), 238-255.
doi: 10.1037/mot0000044 URL |
| [19] |
Gable, P. A., Wilhelm, A. L., & Poole, B. D. (2022). How Does Emotion Influence Time Perception? A Review of Evidence Linking Emotional Motivation and Time Processing. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 848154.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.848154 URL |
| [20] |
Gil, S., & Droit-Volet, S. (2009). Time perception, depression and sadness. Behavioural processes, 80(2), 169-176.
doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2008.11.012 pmid: 19073237 |
| [21] |
Grommet, E. K., Droit-Volet, S., Gil, S., Hemmes, N. S., Baker, A. H., & Brown, B. L. (2011). Time estimation of fear cues in human observers. Behavioural Processes, 86(1), 88-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2010.10.003 pmid: 20971168 |
| [22] | Hengstler, M., Holland, R. W., van Steenbergen, H., & van Knippenberg, A. (2014). The influence of approach-avoidance motivational orientation on conflict adaptation. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(2), 548-560. |
| [23] | Juncai, S., Jing, Z., & Rongb, S. (2017). Differentiating recognition for anger and fear facial expressions via inhibition of return. Journal of Psychology and Cognition, 2(1), 10-16. |
| [24] |
Lake, J. I., LaBar, K. S., & Meck, W. H. (2016). Emotional modulation of interval timing and time perception. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 64, 403-420.
doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.003 URL |
| [25] |
Langer, J., Wapner, S., & Werner, H. (1961). The effect of danger upon the experience of time. The American journal of psychology, 74(1), 94-97.
doi: 10.2307/1419830 URL |
| [26] | Liu, Y. (2015). Attentional bias to motivation related emotional stimuli and its processing mechanism (Doctoral Dissertation), Shanxi Normal University, Xian, China. |
| [27] |
Liu, J. Y., & Li, H. (2019). How state anxiety influences time perception: Moderated mediating effect of cognitive appraisal and attentional bias. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 51(7), 747-758.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2019.00747 |
| [28] |
Liu, J. Y., Huang, X. T., & Yang, S. (2013). Three Components of Attentional Bias in Social Anxiety Disorder. Advances in Psychological Science, 21(4), 664-670.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2013.00664 |
| [29] | Lui, M. A., Penney, T. B., & Schirmer, A. (2011). Emotion Effects on Timing: Attention versus Pacemaker Accounts. PLoS ONE, 6(7), e21829. |
| [30] |
Mella, N., Conty, L., & Pouthas, V. (2011). The role of physiological arousal in time perception: psychophysiological evidence from an emotion regulation paradigm. Brain and cognition, 75(2), 182-187.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2010.11.012 pmid: 21145643 |
| [31] |
Mioni, G., Stablum, F., Prunetti, E., & Grondin, S. (2016). Time perception in anxious and depressed patients: A comparison between time reproduction and time production tasks. Journal of Affective Disorders, 196, 154-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.02.047 pmid: 26922144 |
| [32] |
Moser, J. S., Hajcak, G., & Simons, R. F. (2005). The effects of fear on performance monitoring and attentional allocation. Psychophysiology, 42(3), 261-268.
pmid: 15943679 |
| [33] |
Noulhiane, M., Mella, N., Samson, S., Ragot, R., & Pouthas, V. (2007). How emotional auditory stimuli modulate time perception. Emotion, 7(4), 697-704.
pmid: 18039036 |
| [34] |
O’Connell, R. G., Bellgrove, M. A., Dockree, P. M., Lau, A., Fitzgerald, M., & Robertson, I. H. (2008). Self-alert training: Volitional modulation of autonomic arousal improves sustained attention. Neuropsychologia, 46(5), 1379-1390.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.12.018 pmid: 18249419 |
| [35] |
Ochsner, K. N., & Gross, J. J. (2005). The cognitive control of emotion. Trends in cognitive sciences, 9(5), 242-249.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.03.010 pmid: 15866151 |
| [36] | O'Toole, L. J., DeCicco, J. M., Hong, M., & Dennis, T. A. (2011). The impact of task-irrelevant emotional stimuli on attention in three domains. Emotion, 11(6), 1322. |
| [37] |
Posner, M. I., & Petersen, S. E. (1990). The attention system of the human brain. Annual review of neuroscience, 13(1), 25-42.
doi: 10.1146/neuro.1990.13.issue-1 URL |
| [38] |
Sarapas, C., Weinberg, A., Langenecker, S. A., & Shankman, S. A. (2017). Relationships among attention networks and physiological responding to threat. Brain and Cognition, 111, 63-72.
doi: S0278-2626(16)30263-9 pmid: 27816781 |
| [39] |
Sarigiannidis, I., Grillon, C., Ernst, M., Roiser, J. P., & Robinson, O. J. (2020). Anxiety makes time pass quicker while fear has no effect. Cognition, 197, 104116.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.104116 URL |
| [40] |
Tapper, K., Pothos, E. M., & Lawrence, A. D. (2010). Feast your eyes: hunger and trait reward drive predict attentional bias for food cues. Emotion, 10(6), 949-954.
doi: 10.1037/a0020305 pmid: 21058840 |
| [41] | Techer, F., Jallais, C., Fort, A., & Corson, Y. (2015). Assessing the impact of anger state on the three Attentional Networks with the ANT-I. Emotion, 15(3), 276. |
| [42] |
Thoma, P., Bauser, D. S., & Suchan, B. (2013). BESST (Bochum Emotional Stimulus Set)—A pilot validation study of a stimulus set containing emotional bodies and faces from frontal and averted views. Psychiatry Research, 209(1), 98-109.
doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.11.012 URL |
| [43] |
Tracy, J. L. (2014). An evolutionary approach to understanding distinct emotions. Emotion Review, 6(4), 308-312.
doi: 10.1177/1754073914534478 URL |
| [44] | Yin, H. Z., Bai, Y. L., Liu, S. G., & Li, D. (2021). The Influence of Motivation Direction and Intensity on Time Perception in Positive and Negative Emotions. Journal of Psychological Science, 44(6), 1313-1321. |
| [45] |
Yin, H. Z., Cui, X. B., Bai, Y. L., Cao, G.G., Deng, J. X., & Li, D. (2020). The important time parameters and related evidences from dual perspectives of temporal information processing and temporal processing of information. Advances in Psychological Science, 28(11), 1853-1864.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2020.01853 |
| [46] | Yin, H. Z., Zhang, L., & Li, D. (2023). The influence of emotion on time perception: The perspective of non-embodied emotion view and embodied emotion view. Journal of Psychological Science, 46(2), 491-499. |
| [47] | Yu, X. L. (2017). Characteristics and Neural Mechanisms of Attention Bias and Attentional Control in Social Anxiety Individuals and the Exploration on Their Relationship. (Doctoral Dissertation), Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China. |
| [48] | Yu, Y. J. (2020). Effects of Anxiety and Depression on Attentional Bias: The Mediating Role of Attentional Control. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 18(1), 121-127. |
| [49] |
Zakay, D., & Block, R. A. (1997). Temporal Cognition. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 6(1), 12-16.
doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.ep11512604 URL |
| [50] | Zhang, L. H., & Duan, C. B. (2022). Attention bias and attention control under emotional priming in different types of high self-esteem individuals. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 36(03), 248-254. |
| [51] |
Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Zhao, S. Y., & Li, H. (2014). Attentional Bias towards Threat: Facilitated Attentional Orienting or Impaired Attentional Disengagement? Advances in Psychological Science, 22(7), 1129-1138.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.01129 |
| [1] | TIAN Yangyang, LI Dong, YAN Xiangbo, LI Zhao, CUI Qian, JIANG Zhongqing. The representational momentum effect and the reference dependence effect on the evaluation of dynamic happy expressions [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2024, 56(1): 29-43. |
| [2] | CHEN Peiqi, ZHANG Yinling, HU Xinmu, WANG Jing, MAI Xiaoqin. The effect of social value orientation on third-party altruistic behaviors in children aged 10-12 years: The role of emotion [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(8): 1255-1269. |
| [3] | WANG Mei, CHENG Si, LI Yiwei, LI Hong, ZHANG Dandan. The role of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on placebo effect of regulating social pain: A TMS study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(7): 1063-1073. |
| [4] | ZHU Yanghao, LONG Lirong, LIU Wenxing. Can leader gratitude expression improve employee followership behavior? The role of emotional expression authenticity [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(7): 1160-1175. |
| [5] | XIE Hui, LIN Xuanyi, HU Wanrou, HU Xiaoqing. Emotion regulation promotes forgetting of negative social feedback: Behavioral and EEG evidence [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(6): 905-919. |
| [6] | DING Yuting, ZHANG Chang, LI Ranran, DING Wenyu, ZHU Jing, LIU Wei, CHEN Ning. The influence of positive co-experience on teacher-student relationship: The mediating role of emotional bonding [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(5): 726-739. |
| [7] | LI Liyuan, GAO Xiangyu, ZHENG Xiaoming. An examination of configural effects of employees’ proactive behavior: A process perspective [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(5): 792-811. |
| [8] | JI Li-Jun, WU Ying, YANG Yiyin. The breath of temporal information focus among Chinese people [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(3): 421-434. |
| [9] | ZHENG Xi, ZHANG Tingting, LI Liang, FAN Ning, YANG Zhigang. Unmasking effects of speech emotional prosody and semantics on auditory informational masking [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(2): 177-191. |
| [10] | WANG Xiaoqin, TAN Yafei, MENG Jie, LIU Yuan, WEI Dongtao, YANG Wenjing, QIU Jiang. The influence of emotion regulation flexibility on negative emotions: Evidence from experience sampling [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(2): 192-209. |
| [11] | GAO Kexiang, ZHANG Yueyao, LI Sijin, YUAN Jiajin, LI Hong, ZHANG Dandan. Ventromedial prefrontal cortex plays a critical role on implicit emotion regulation: A tDCS study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(2): 210-223. |
| [12] | WANG Hailing, CHEN Enguang, LIAN Yujing, LI Jingjing, WANG Liwei. Automatic processing of facial width-to-height ratio [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(11): 1745-1761. |
| [13] | SU Jiajia, YE Haosheng. Extended Mind: Is the brain the sole basis for realizing the mind? [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(11): 1889-1902. |
| [14] | HUANG Xinjie, ZHANG Chi, WAN Huagen, ZHANG Lingcong. Effect of predictability of emotional valence on temporal binding [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(1): 36-44. |
| [15] | SUN Bo, ZENG Xianqing, XU Kaiyu, XIE Yunting, FU Shimin. Neural correlates of consciousness of emotional faces and the unconscious automatic processing: Evidence from event-related potentials (ERPs) [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(8): 867-880. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||